In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology and networking, ensuring the seamless flow of data and maintaining optimal performance are critical challenges. One key solution that has emerged to address these concerns is the implementation of load balancer network. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of load balancers, their significance in modern IT infrastructures, and the best practices for their deployment.
_preview.jpg)
Introduction:
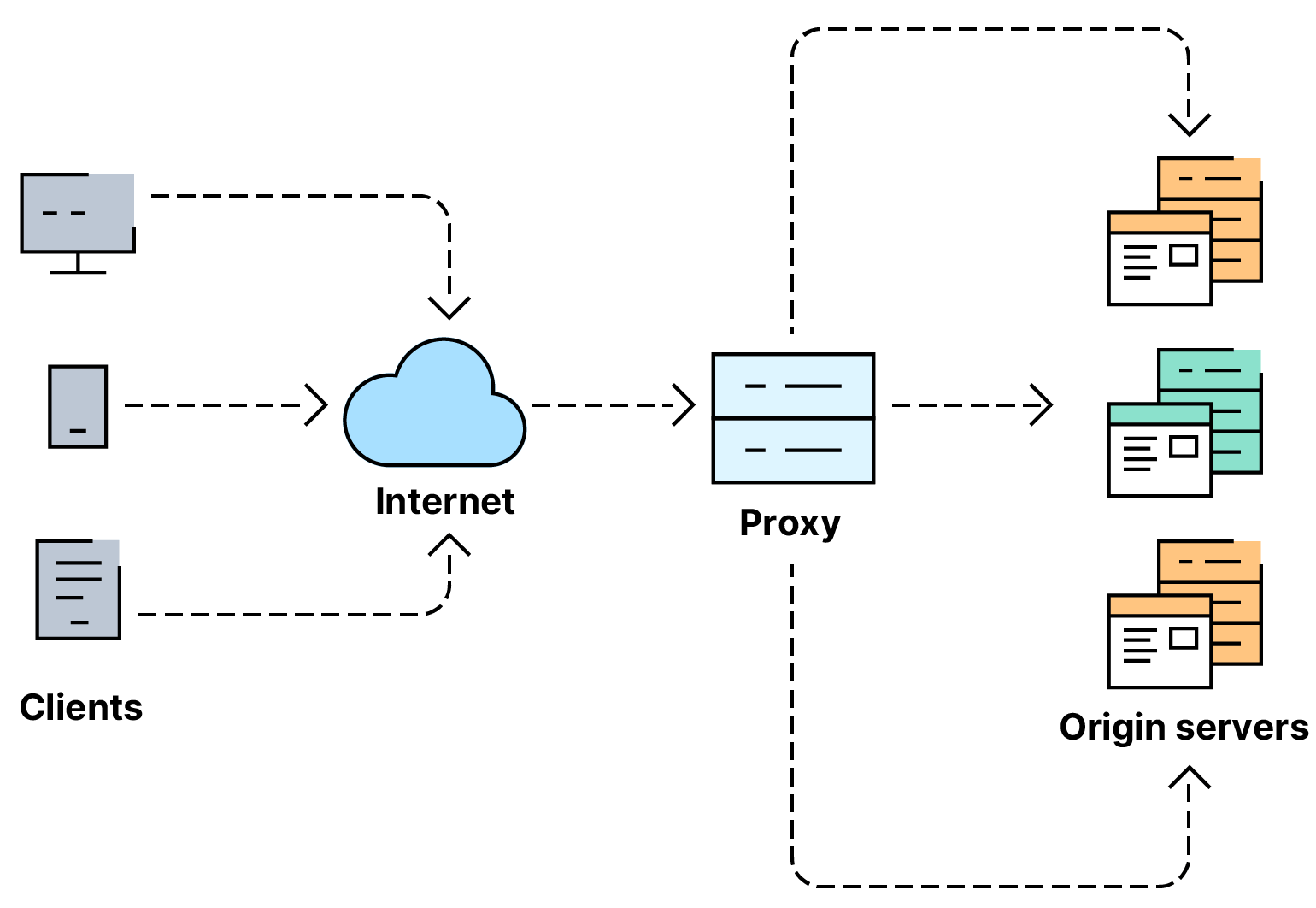
In the realm of network architecture, a load balancer plays a pivotal role in distributing incoming network traffic across multiple servers. The primary objective is to prevent any single server from being overwhelmed with too much demand, thereby optimizing resource utilization, enhancing fault tolerance, and ensuring high availability.
Understanding Load Balancer Networks:
A load balancer acts as a traffic manager, efficiently distributing incoming requests among a pool of servers. By doing so, it prevents any single server from becoming a bottleneck and helps maintain a consistent and responsive user experience. Load balancing can be implemented at various layers of the OSI model, including the application layer, transport layer, and network layer, depending on the specific requirements of the system.
Key Benefits of Load Balancers:
- Scalability: Load balancers enable horizontal scaling by efficiently distributing traffic among multiple servers, allowing organizations to expand their infrastructure as demand grows.
- Fault Tolerance: In the event of a server failure, a load balancer redirects traffic to healthy servers, ensuring continuous service availability and minimizing downtime.
- Performance Optimization: By distributing traffic intelligently, load balancers help prevent server overload, ensuring that each server operates within its capacity for optimal performance.
- Security: Load balancers can enhance security by acting as a barrier against certain types of cyber threats, such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, and providing features like SSL termination for secure communication.
- Session Persistence: Some applications require that a user's session remain connected to the same server throughout their interaction. Load balancers can be configured to maintain session persistence, ensuring a seamless user experience.
Types of Load Balancers:
- Hardware Load Balancers: These are physical devices dedicated to the task of load balancing. They often provide high performance and advanced features but can be costlier.
- Software Load Balancers: Running as software on standard servers, these load balancers are a cost-effective alternative. They are highly configurable and suitable for virtualized environments.
- Cloud-Based Load Balancers: Designed for cloud environments, these load balancers offer scalability and flexibility, automatically adjusting to changing workloads.
Best Practices for Load Balancer Deployment:
- Understanding Workload Distribution: Analyze traffic patterns and user behavior to determine the optimal distribution of workloads across servers.
- Regular Monitoring and Scaling: Implement monitoring tools to track server performance and scale resources dynamically based on demand.
- Geographic Load Balancing: For global applications, consider implementing load balancing across multiple geographic locations to reduce latency and improve user experience.
- SSL Offloading: Offload SSL/TLS encryption and decryption tasks to the load balancer to reduce the processing burden on application servers.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep load balancer software up-to-date to ensure compatibility with the latest security protocols and features.
Conclusion:
As organizations continue to embrace digital transformation, the importance of load balancer network cannot be overstated. Whether in on-premises data centers or cloud environments, load balancers play a crucial role in optimizing performance, enhancing reliability, and ensuring a seamless user experience. By understanding the principles behind load balancing and implementing best practices, businesses can build robust and scalable infrastructures that meet the demands of today's dynamic and interconnected world.